Dose Response with the RNA Interference Therapy
Dose Response with the RNA Interference Therapy JNJ-3989 Combined with Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Treatment in Expanded Cohorts of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Current therapies for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) are a nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA; tenofovir disoproxil [TDF], tenofovir alafenamide, or entecavir [ETV]) or sometimes pegylated interferon.1,2
- After five years on NA monotherapy, only 0–3% of patients will achieve a functional cure, defined clinically as hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) loss with or without anti-HBs seroconversion.1–3
- RNA interference (RNAi) therapy silences HBV RNA transcripts thereby reducing HBsAg and all other viral products and has demonstrated promising activity as a potential component of finite therapy for CHB patients.4–6
- JNJ-73763989 (JNJ-3989; ARO-HBV) was designed to silence HBV RNA transcripts from episomal cccDNA and host-integrated HBV DNA.
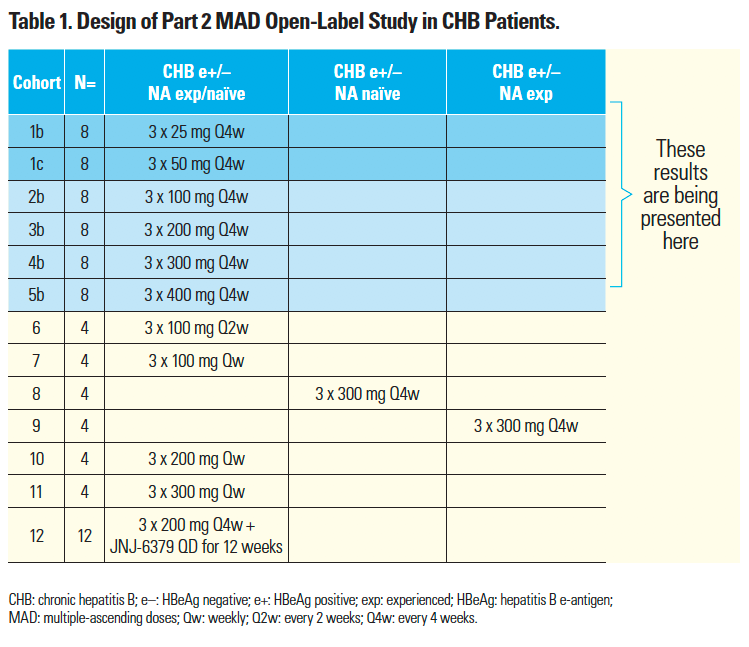
- In part 2 of the study AROHBV1001 (NCT03365947)⁷ in CHB patients, JNJ-3989 reduced serum HBsAg levels by ≥1 log10 in all patients receiving three JNJ-3989 doses (100–400 mg, one every 4 weeks [Q4w]) with an NA (TDF or ETV), regardless of baseline hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg) status or prior NA therapy.7
- Given the lack of a dose response with 100–400 mg Q4w JNJ-3989,⁷ cohorts 2b–5b (Table 1) were expanded from four to eight patients, and two lower dose cohorts 1b and 1c (25 and 50 mg Q4w, respectively) were added to study AROHBV1001.
- Efficacy data up to Day 113 are presented (i.e. two months post JNJ-3989 dosing) for cohorts 2b–5b (100–400 mg Q4w JNJ-3989), and cohorts 1b and 1c (Table 1), and safety data are shown through Day 113.
