Establishing baseline framework for hepatitis B virus in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Establishing baseline framework for hepatitis B virus micro-elimination in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam – a community-based seroprevalence study
Summary
Background
We conducted a community-based seroprevalence study using three HBV seromarkers (HBsAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc) in Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC), Vietnam, to (1) determine the prevalence of HBV serologic profiles; (2) document factors associated with HBV infection or susceptibility; and (3) propose strategies toward HBV elimination by 2030.
Methods
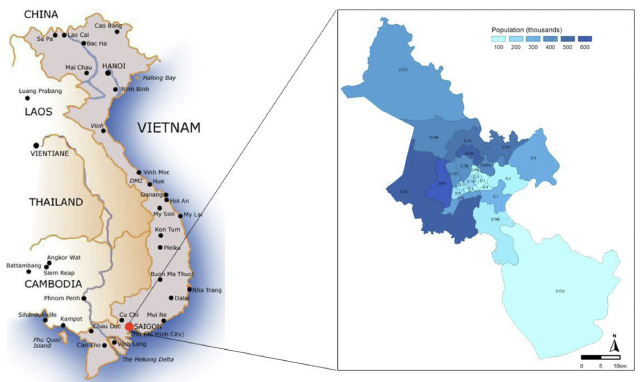
During 2019–2020, we deployed a multistage cluster design with probability proportionate to size, to recruit 20,000 adults for an HBV screening and linkage to care program citywide. Screening results with interpretation, recommendations, and health education materials were returned to participants. Post-study surveys were conducted within three months to identify gaps in linkage to care.
Findings
Of the 17,600 adults invited, 15,275 (86.7%) participated in the study, 14,674 (96.1%) completing all data for final analyses. The prevalence of HBsAg (+) and HBV-naïve were 7.5% and 37.7%, respectively. HBV vaccination rates were 18.7% and about 50% of HCMC population had been exposed to HBV. Of the persons with HBsAg (+), 27.1% linked to care (76% used health insurance). There were wide variations in HBsAg (+) and HBV vaccination rates between districts, risk factors, and socio-economic statuses.
